Python invalid index to scalar variable is an error that might be encountered because various reasons, which we will explore in this article. First, we will discuss this error, its meaning, and why it might occur. Then, we will show some ways to fix this error. Finally, we will offer more information on the topic for those who want to learn more.
Contents
- 1 What Does Python Invalid Index to Scalar Variable Mean?
- 2 Why Does Python Invalid Index to Scalar Variable Occur?
- 3 How To Solve Python Invalid Index to Scalar Variable?
- 4 Conclusion
- 5 References
What Does Python Invalid Index to Scalar Variable Mean?
Python invalid index to scalar variable error means that you are trying to use an index (subscript) on a variable that is not an interable object (for example, an array or a list). Check out subscriptable objects to learn more about interable and subscriptable objects. Consider the following example code:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
print(my_list[0]) # This is valid
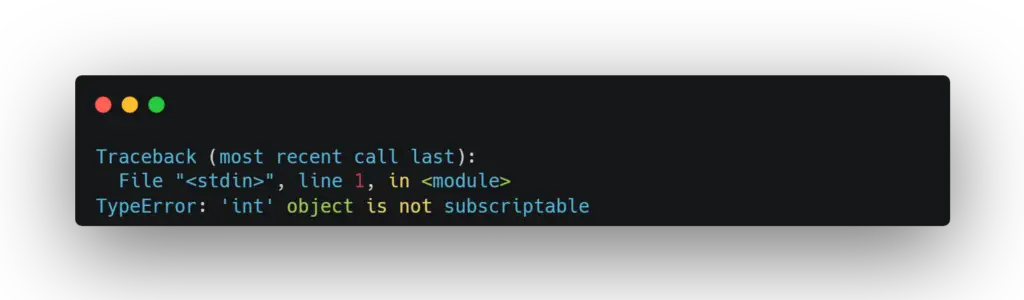
my_scalar = 5
print(my_scalar[0]) # This gives an error because my_scalar is not a listIn the first line of code above, we create a list called my_list. We can then use the square brackets ([ ]) to get the first element of this list (which has an index of 0). However, if we try to do the same thing with a scalar variable (a single value), it will not work because my_scalar is not an interable object is an integer. This is an example of what causes the “invalid index to scalar variable” error.
Why Does Python Invalid Index to Scalar Variable Occur?
This error might occur in your code for a few different reasons. For example, you might accidentally try to use an index on a scalar variable:
my_scalar = 5
print(my_scalar[0]) This will give an error:
In this case, you can remove the square brackets, and the code will work as expected:
my_scalar = 5
print(my_scalar) # Prints 5 (without using an index)Another common error while dealing with lists is using an index that is out of bounds for the list or array you are trying to access. For example, consider the following code:
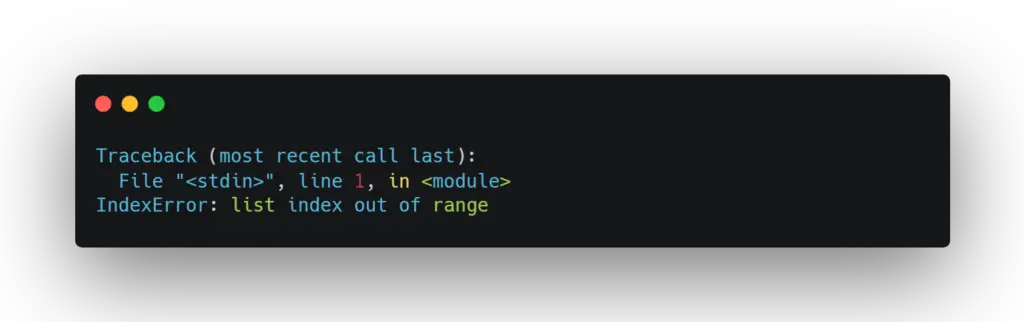
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
print(my_list[3]) This will give an error because my_list only has three elements
This code gives an error because we are trying to access the fourth element of my_list (which has an index of 3), but our list only has three elements. To fix this, we need to ensure that we use an index within our list’s bounds.
There are a few different ways to solve this error, depending on the cause. If you are accidentally trying to use an index on a scalar variable, you can remove the square brackets, and the code will work as expected:
my_scalar = 5
print(my_scalar) # Prints 5 (without using an index)
If you are using an index that is out of bounds for the list or array you are trying to access, you need to make sure that you are using an index that is within the bounds of your list. For example, if we want to print the third element of our my_list list from the previous section; we would do it like this:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
print(my_list[2]) # Prints 3 (which is the third element in our list)Finally, if you are trying to use an index on a variable that is not an interable object, For example, if we want to use our my_list list from the previous section, we would do it like this:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
print(my_list[0]) # Prints 1 (which is the first element in our list)Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the “invalid index to scalar variable” error in Python. We have seen this error and why it might occur in your code. Finally, we have provided some tips on how to solve it.
References
- Python Documentation
To learn more, please follow pythonclear
Indexing is one of the most important concepts when we talk about large data with a linear data structure. It is equally essential to understand how we have to use indexes to feature our data and deal with data for actual use. In this article, we will deal with the topic of solving invalid indexes to the scalar variable.
What is an «invalid index to scalar variable» error?
It is a compile-time error that occurs when the programmer does not put the correct index position or dimension-tier ( [][] ) while accessing any list value from the list. Dimension tier is the number of square brackets we have to use with the variable or identifier’s name to fetch any particular value from that list. If we talk about Python, it is essential to know how the square brackets work while fetching any particular value from a list or nested list. If the programmer does any kind of mistake, then we might encounter this «invalid index to scalar variable” error.
Let us now Practically see this in action:
If you have a situation with a code
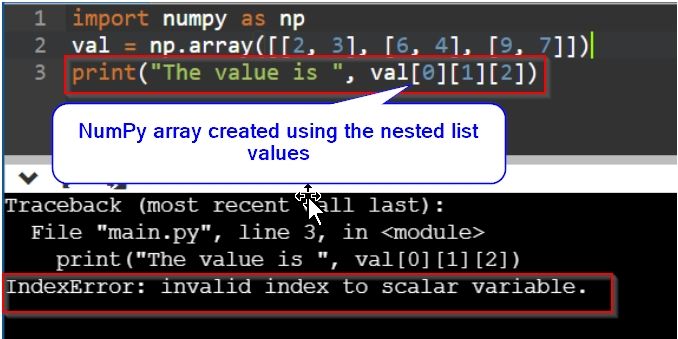
import numpy as np
val = np.array([[2, 3], [6, 4], [9, 7]])
print("The value is ", val[0][1][2])And you want to display a specific value from the NumPy array created using the nested list values.
You can see, the program is showing the invalid index to scalar variable error. It is because the NumPy array defined here has a dimension of two. This means, only two indices are enough to represent any particular value from the NumPy array created from a nested list. But here, within the print(), we are using three tier indexing which is not appropriate.
This is the reason why this program is showing such error.
How to Solve it?
There are two ways of solving such issues.
1st way:
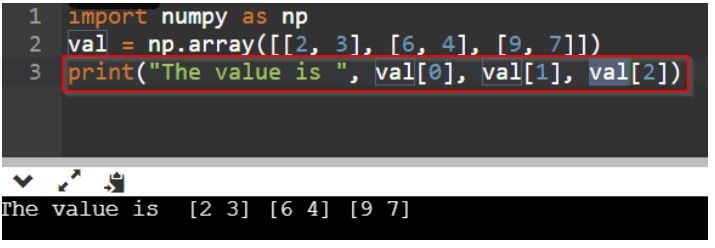
import numpy as np
val = np.array([[2, 3], [6, 4], [9, 7]])
print("The value is ", val[0], val[1], val[2])Explanation:
Doing this will make the Python interpreter understand that each of the values within the pair of square brackets represent index 0, 1, and 2 respectively. So, calling them directly using the single tier value will fetch the lists residing inside the ndarray.
2nd way:
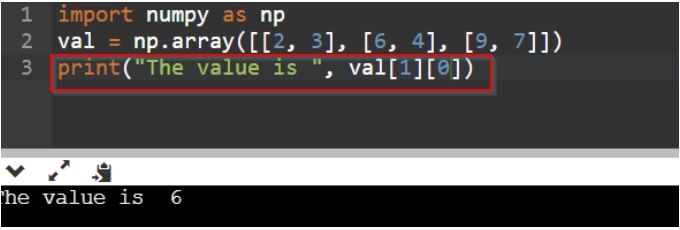
import numpy as np
val = np.array([[2, 3], [6, 4], [9, 7]])
print("The value is ", val[1][0]) // val[1st sq. bracket][2nd sq. bracket]This is the other way of doing this. Here, we are using two-tier since the NumPy array is a two dimensional array of data nested in a single layer. This will fetch the value 6 because the first square bracket indicates the [2, 3] => index 0, [6, 4] => index 1, and [9, 7] => index 2
The second square bracket represent the values inside it. [6 => sub index 0, 4 => sub index 1]
Conclusion:
To solve the invalid index to scalar variable error, programmers must keep a close eye at writing the index value and number of square brackets. If the number of square brackets is not appropriate or an anomaly occurs (the declaration and definition have two-dimensional NumPy array that uses a 3-tier indexing), then there is a possibility of index scalar variable error. Hence, it is also essential to know the different ways of representing and accessing NumPy arrays data from a defined variable.
IndexError is an exception error in python you get when you try to index the list or array and the length of it is out of the range. Most programmers get this type of error while accessing the element from the array or list. In this tutorial, you will know how to solve the IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable error in a simple way.
Why does the IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable Error occurs?
Most of the time you will get the error when you are trying to wrongly access the element of the array. For example, you have created a variable of scalar type but you are indexing the element like the two or more dimensions.
Let’s understand it deeply. Suppose I have created a scalar value in numpy. If I am trying to access it wrongly then I will get the invalid index to scalar variable error.
You will get the error when you will run the below lines of code.
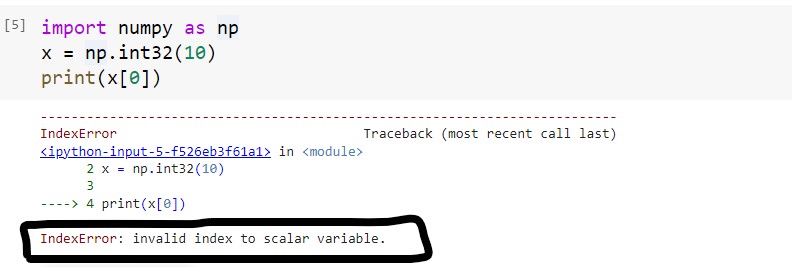
import numpy as np
x = np.int32(10)
print(x[0])Output
In the same way, you will get the invalid index to the scalar variable when you try to access the element of the numpy array like it is a multi-dimensional array.
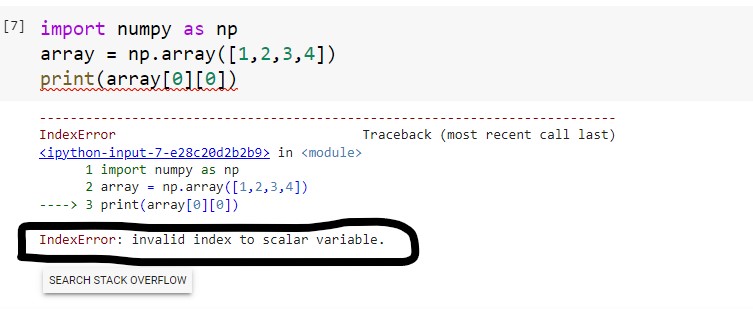
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print(array[0][0])Output
Solution of the invalid index to scalar variable Error
The solution to this indexerror is very simple. Make sure to identify the type of the array whether it is a scalar and single-dimensional or multi-dimensional array.
Taking the same example as the above, you don’t have to use the index in the square bracket to access the value. You can access directly using the variable name only.
import numpy as np
x = np.int32(10)
print(x)Output
10And if it is an array of single-dimensional then don’t use the square bracket two times to access the element. Just use the single square bracket with the index inside it.
import numpy as np
array = np.array([1,2,3,4])
print(array[0])Output
1Conclusion
In the name itself IndexError you can get the idea of why you are getting the error. Most of cases the error are due to wrong accessing of the element. The error index to a scalar variable is the same. To solve this error you have first identified the element is of scalar or another dimension and then use the correct way to access it.
I hope you have liked this tutorial. If you have any queries then you can contact us for more help.
Join our list
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting stuff and updates to your email inbox.
We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously
Thank you for signup. A Confirmation Email has been sent to your Email Address.
Something went wrong.
When working with the NumPy library, you might encounter this error:
IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable
This error usually occurs when you used an index to access a scalar variable.
A scalar is a variable that holds one value at a time, which is different from vectors that can hold multiple values.
This tutorial will show you examples that cause this error and how to fix it.
How to reproduce this error
Suppose you used NumPy to create an array as follows:
import numpy as np
numbers = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
The numbers variable is a one-dimensional array containing int values. It’s a vector variable because it holds multiple values.
Next, let’s say you want to access the first two items in the array, so you use the square brackets like this:
Output:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "main.py", line 5, in <module>
print(numbers[0][0])
IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable.
The error above indicates that you’re trying to access a scalar variable, which holds only one value, with an index number.
The syntax numbers[0][1] has one extra square brackets notation that causes this error.
Here’s another example that’s easier to understand:
import numpy as np
numbers = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
value = numbers[0] # 1
item = value[1] # ❌
In the above example, the value variable is a scalar variable because it holds only one value: the first item in the numbers variable.
In the last line, we declared the item variable to hold the second item of the value variable, and this causes the error.
How to fix this error
To resolve this error, you need to correct the syntax to access the items in your array.
If you want to access the first two items in the array, the correct way is to access one item at a time like this:
import numpy as np
numbers = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(numbers[0]) # 1
print(numbers[1]) # 2
# or
print(numbers[0], numbers[1]) # 1 2
Using double square brackets notation as in numbers[0][1] only works when you have a multi-dimensional array.
Here’s an example of a two-dimensional array:
import numpy as np
pairs = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
## Access the arrays inside pairs
print(pairs[0]) # [1, 2]
print(pairs[1]) # [3, 4]
print(pairs[0][0]) # 1
print(pairs[0][1]) # 2
print(pairs[1][0]) # 3
print(pairs[1][1]) # 4
In the above example, the pairs array consists of an array that has two child arrays.
You can access the child array’s item using double square brackets.
As long as you’re not trying to access a scalar variable with square brackets notation, this error won’t appear.
Conclusion
The error IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable occurs when you try to access a scalar variable using the square brackets notation.
The square brackets notation is used to access items in vector variables, which can hold multiple values.
Because scalar variables can only have a single value, the fact that you’re using index numbers to access a scalar variable is what Python is complaining about.
I hope this tutorial is helpful. Happy coding! 🙏
import numpy as np
with open('matrix.txt', 'r') as f:
x = []
for line in f:
x.append(map(int, line.split()))
f.close()
a = array(x)
l, v = eig(a)
exponent = array(exp(l))
L = identity(len(l))
for i in xrange(len(l)):
L[i][i] = exponent[0][i]
print L
-
My code opens up a text file containing a matrix:
1 2
3 4
and places it in listxas integers. -
The list
xis then converted into an arraya. -
The eigenvalues of
aare placed inland the eigenvectors are placed inv. -
I then want to take the exp(a) and place it in another array
exponent. -
Then I create an identity matrix
Lof whatever lengthlis. -
My for loop is supposed to take the values of
exponentand replace the 1’s across the diagonal of the identity matrix but I get an error sayinginvalid index to scalar variable.
What is wrong with my code?
asked Nov 27, 2012 at 22:42
1
exponent is a 1D array. This means that exponent[0] is a scalar, and exponent[0][i] is trying to access it as if it were an array.
Did you mean to say:
L = identity(len(l))
for i in xrange(len(l)):
L[i][i] = exponent[i]
or even
L = diag(exponent)
?
answered Nov 27, 2012 at 22:45
NPENPE
487k108 gold badges951 silver badges1013 bronze badges
0
IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable happens when you try to index a numpy scalar such as numpy.int64 or numpy.float64. It is very similar to TypeError: 'int' object has no attribute '__getitem__' when you try to index an int.
>>> a = np.int64(5)
>>> type(a)
<type 'numpy.int64'>
>>> a[3]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: invalid index to scalar variable.
>>> a = 5
>>> type(a)
<type 'int'>
>>> a[3]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'int' object has no attribute '__getitem__'
answered Sep 19, 2013 at 20:36
AkavallAkavall
82.7k51 gold badges207 silver badges251 bronze badges
1
In my case, I was getting this error because I had an input named x and I was creating (without realizing it) a local variable called x. I thought I was trying to access an element of the input x (which was an array), while I was actually trying to access an element of the local variable x (which was a scalar).
answered Apr 7, 2020 at 19:46
nbronbro
15.4k32 gold badges113 silver badges197 bronze badges