I’m trying to enable dhcp for ipv6 with the «ipv6 dhcp relay dest» command but, I’m receiving an error and I’m trying both of these commands but none work.
Router model: 2811
(config)# interface [interface-1]
(config-if)# ipv6 dhcp destination [destination ipv6 address]
[interface-2]
and
interface type number
ipv6 dhcp relay destination ipv6-address [interface-type interface-number]
Error:
% Invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker.
Source
Ron Maupin♦
98.3k26 gold badges116 silver badges191 bronze badges
asked Dec 1, 2018 at 2:55
2
The 2811 router is fairly old and End-of-Life since 2016, with the last software updates in 2014 (over four years ago). Your IOS version probably does not support this command. You always need to look at the IOS versions where the command was introduced:
Cisco IOS IPv6 Command Reference — ipv6 dhcp relay destination
Also, this does not seem like a CCNA-level subject, and it may not be supported by Packet Tracer, which is an emulator that is limited in what it supports. A real 2811 may be able to run the correct IOS version (or it may not even be available for that EoS router).
answered Dec 1, 2018 at 4:18
Ron Maupin♦Ron Maupin
98.3k26 gold badges116 silver badges191 bronze badges
It’s an old question — but for anyone finding it you should know that the IPv6 relay agent has not been implemented in Packet Tracer for ANY router.
answered Feb 2, 2022 at 17:16
I’m trying to enable dhcp for ipv6 with the «ipv6 dhcp relay dest» command but, I’m receiving an error and I’m trying both of these commands but none work.
Router model: 2811
(config)# interface [interface-1]
(config-if)# ipv6 dhcp destination [destination ipv6 address]
[interface-2]
and
interface type number
ipv6 dhcp relay destination ipv6-address [interface-type interface-number]
Error:
% Invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker.
Source
Related Solutions
Cisco – Access Cisco Call Manager Express on 2811 Router
The dhcp server shows they do actually have an address. The status messages suggest they aren’t able to find all the files they’re looking for; the telephony-service should be creating those, but I don’t see a create cnf-files in your config. show telephony-service tftp-bindings will show what configs it’s created and mapped. The SCCP firmware requires option 66 (tftp server), not option 150 — the phones will remember the last server if dhcp doesn’t present one. (it can be manually configured as well.)
(even without most of the files, it’ll still boot and register with the CM. I was updating eBay’d 7960’s that weren’t known to my CM last night. They only needed to see: OS79XX.TXT, SEPDefault.cnf, and XMLDefault.cnf.xml, and the firmware files)
Routing – HP V1910, VLAN routing – what did I miss
Your problem is, indeed, with routing. Things in VLAN 1 are using 5.1 as the gateway, right? 5.1 doesn’t know about any other internal networks. (i.e. VLAN 10) Likewise, the hosts in VLAN 1 don’t know about VLAN 10.
When clientA tries to ping serverA, the packets go to the ASA and die as it doesn’t know where to send them. (it’s default route would send them to the internet!) When serverA tries to ping clientA, the packets go to the switch and then to clientA, but then the replies, as before, go away.
For this reason, it’s common to keep the «routing hardware» and «hosts» in different networks. VLAN 1 being just the ASA and Switch. And then VLANs 10 and 11 for the two internal networks. The switch would then be the gateway for VLAN 10&11, with it’s default being the ASA. The ASA would have to have static routes added telling it about the internal networks — routed to the switch. Without this, either the ASA has to «hairpin» traffic back to the switch to reach VLAN 10, or every host in VLAN 1 needs its own route to VLAN 10 (via the switch.)
Introduction
The document describes how to configure a Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) as a DHCPv6 relay agent and also covers some basic troubleshooting. In ASA Code Version 9.0 and later, the ASA supports
Prerequisites
Requirements
Cisco recommends that you have knowledge of these topics:
- IPv6 basic concepts
- IPv6 addressing mechanism
- DHCPv6 packet flow
- DHCP relay concepts
Components Used
The information in this document is based on the ASA 5500 Version 9.1.2.
The information in this document was created from the devices in a specific lab environment. All of the devices used in this document started with a cleared (default) configuration. If your network is live, make sure that you understand the potential impact of any command.
Stateful vs Stateless DHCPv6
If you understand the different method of address allocation in IPv6, it helps you understand how the DHCPv6 relay feature works on the ASA. Refre to Dynamic address assignment in IPv6 using SLAAC and DHCP for a introduction to Stateless Address Autoconfiguration (SLAAC) and DHCPv6.
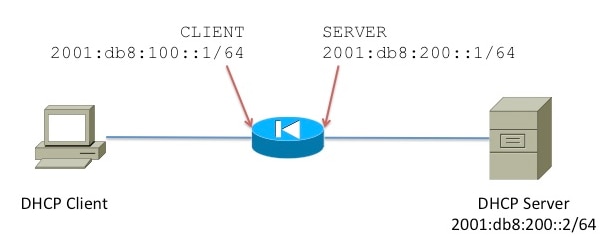
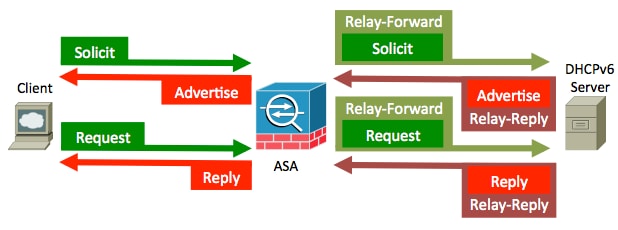
Network Diagram
This sample configuration describes how to configure the ASA as a DHCPv6 relay agent. In this configuration, CLIENT is the interface where the IPv6 client is connected. SERVER is the interface through which the DHCPv6 server 2001:db8:200:2/64 is reachable.
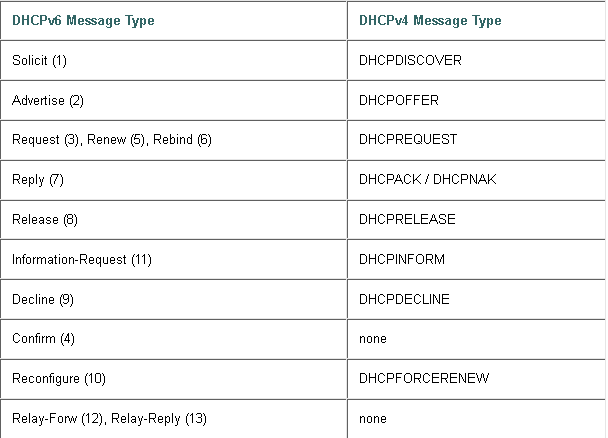
DHCPv6 vs DHCPv4 Message Types
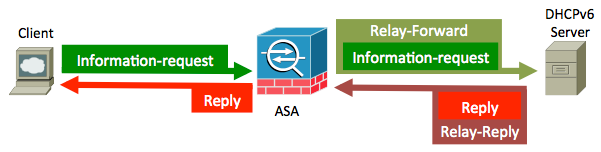
Stateless DHCPv6 Relay
Configuration
Here is the basic configuration for Stateless DHCPv6 relay configuration on the ASA:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif CLIENT
security-level 100
ipv6 address 2001:db8:100::1/64
ipv6 enable
ipv6 nd other-config-flag
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif SERVER
security-level 0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:200:1/64
ipv6 enable
!
ipv6 dhcprelay server 2001:db8:200:2 inside
ipv6 dhcprelay enable outside
Packet Flow
With stateless DHCPv6, here is the packet flow from the client:
The ASA intercepts these packets and wraps them into the DHCP relay format:
Verify
Debugs
If you enable debug ipv6 dhcprelay and debug ipv6 dhcp, then relevant output prints to the screen. This output is taken from a working scenario:
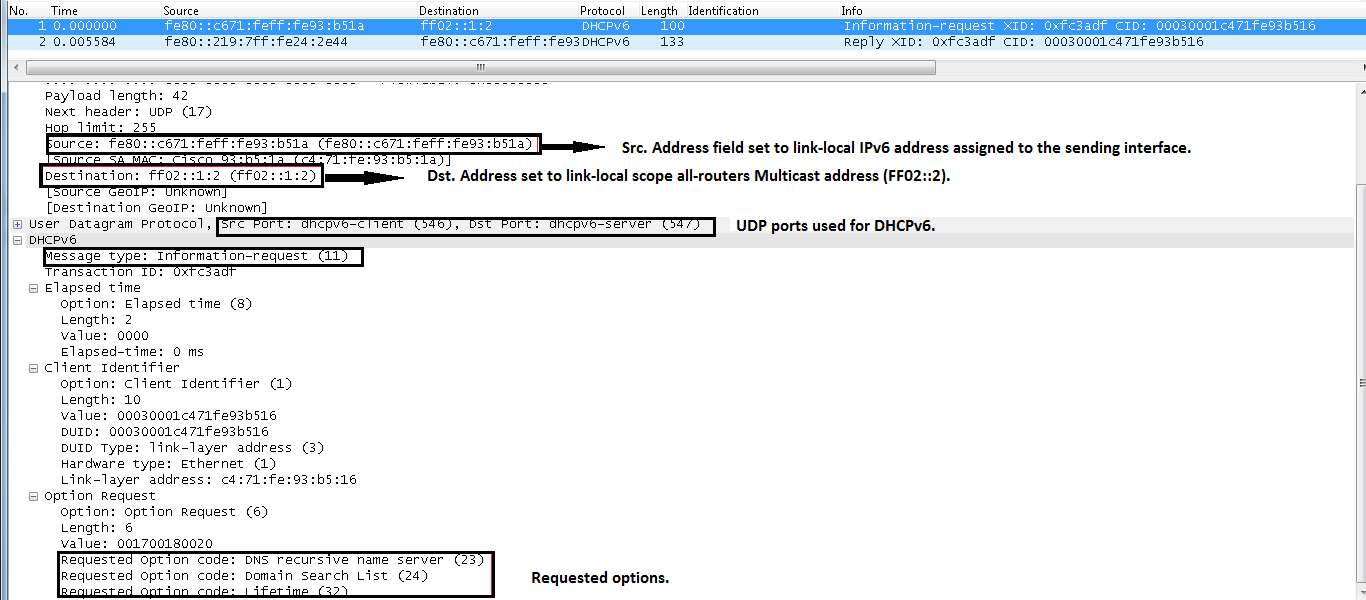
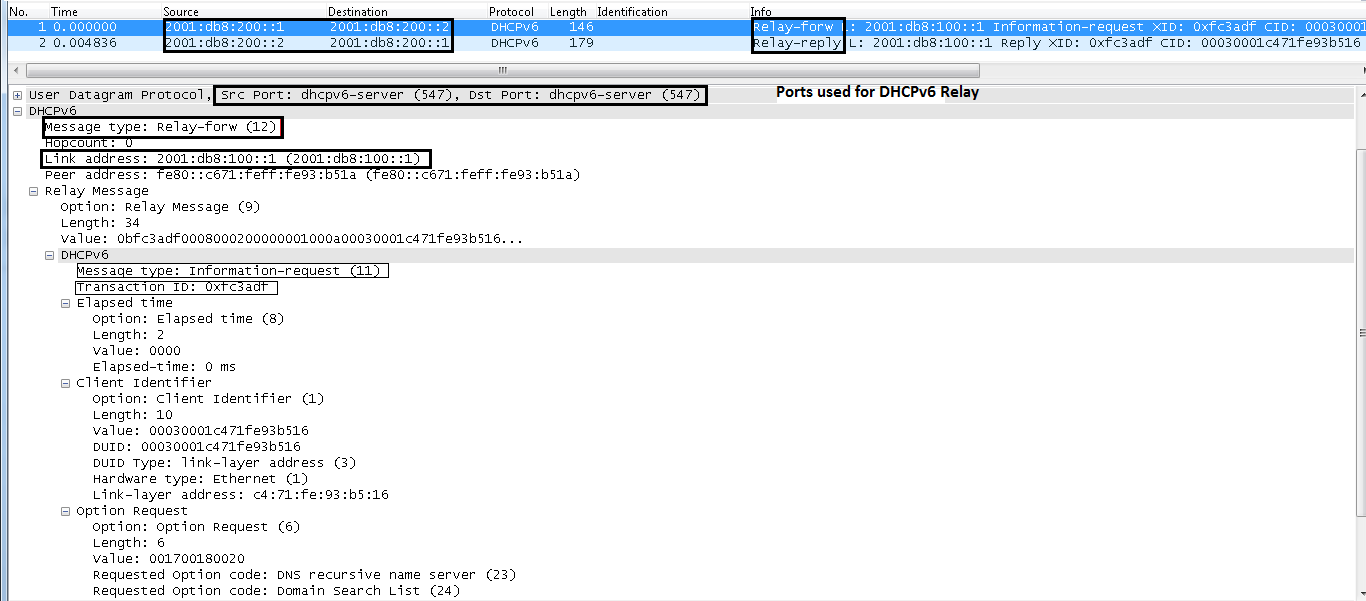
IPv6 DHCP: Received INFORMATION-REQUEST from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
dst ff02::1:2
type INFORMATION-REQUEST(11), xid 1588088
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 6
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST,UNKNOWN
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying INFORMATION-REQUEST from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Creating relay binding for fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a at interface CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to 2001:db8:200::2 via 2001:db8:200::2 using SERVER
IPv6 DHCP: Sending RELAY-FORWARD to 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::1
dst 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
type RELAY-FORWARD(12), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 34
type INFORMATION-REQUEST(11), xid 1588088
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 6
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST,UNKNOWN
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
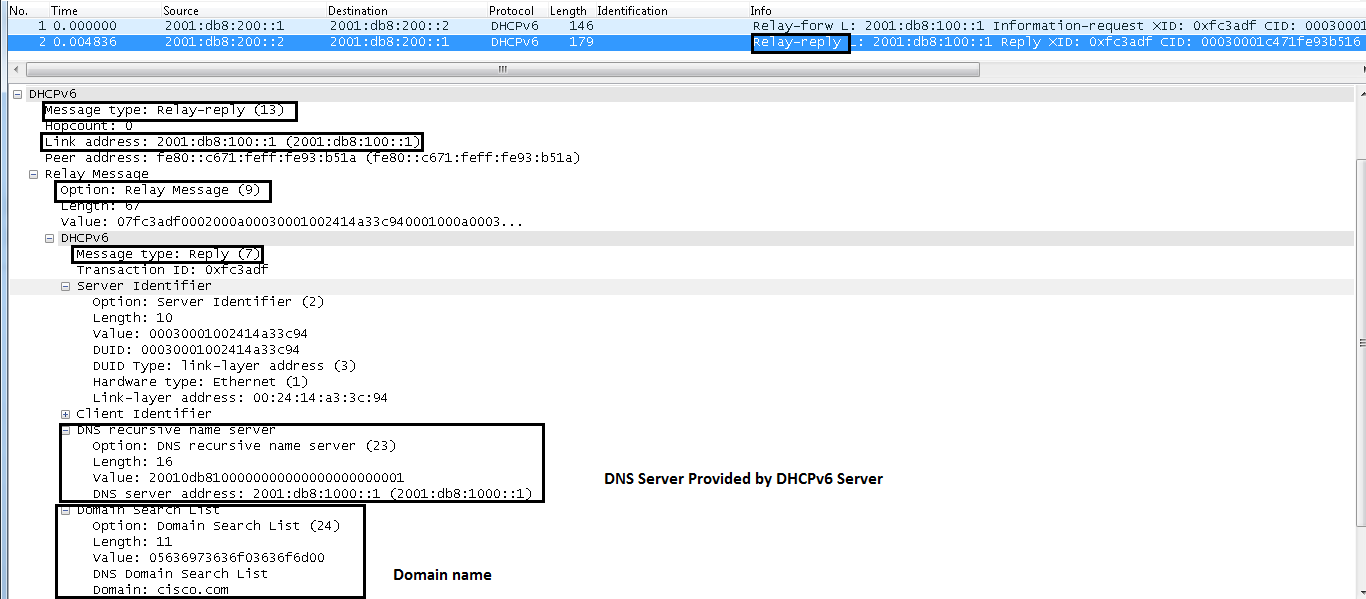
IPv6 DHCP: Received RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
dst 2001:db8:200::1
type RELAY-REPLY(13), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 67
type REPLY(7), xid 1588088
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVER
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: relayed msg: REPLY
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
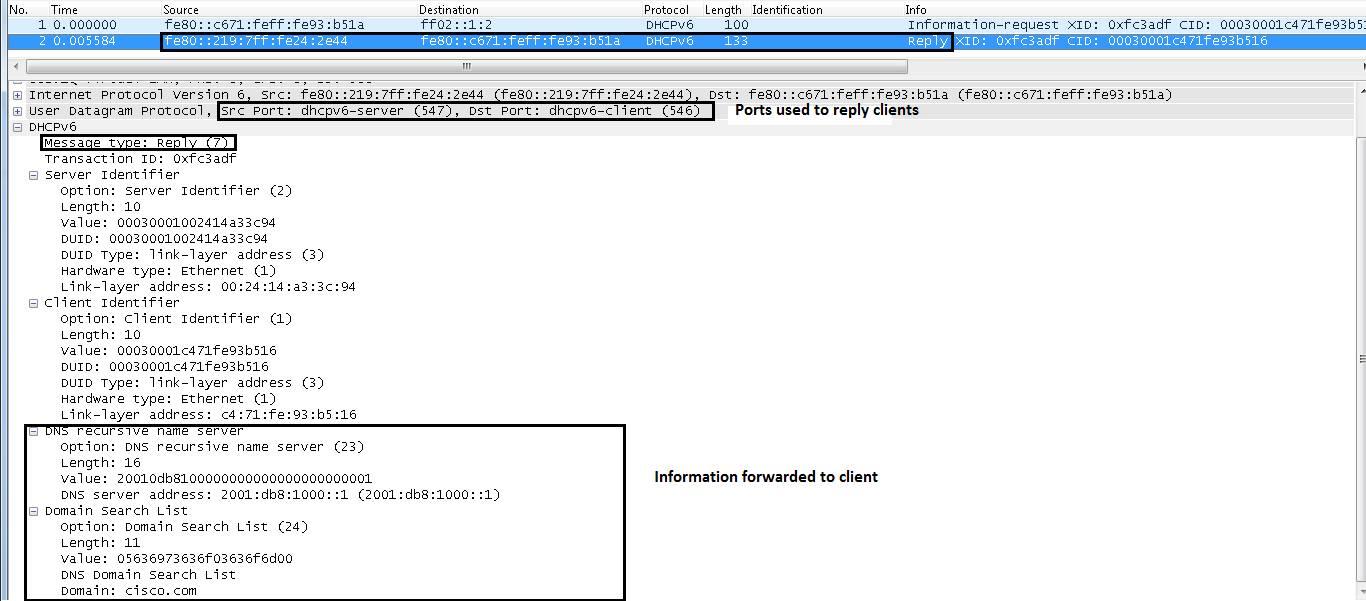
IPv6 DHCP: Sending REPLY to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::219:7ff:fe24:2e44
dst fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
type REPLY(7), xid 1588088
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
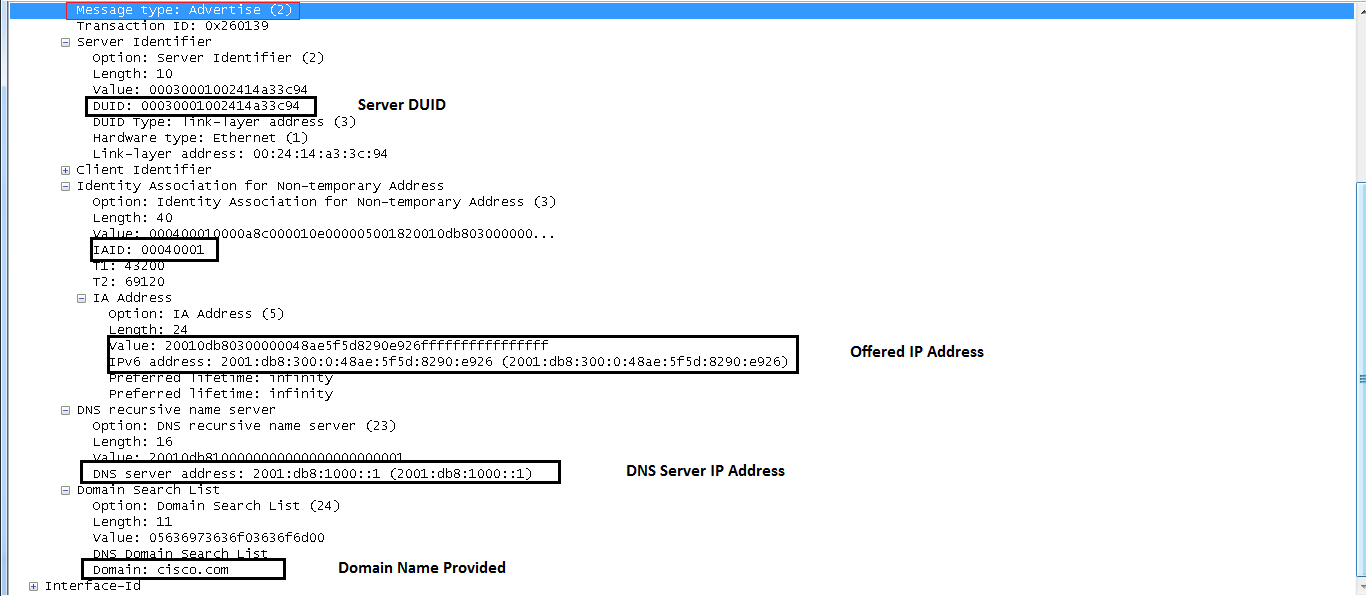
In the INFORMATION-REQUEST request packet, the client only requests DNS-Server and Domain, which is expected since the cilent is configured for stateless DHCPv6.
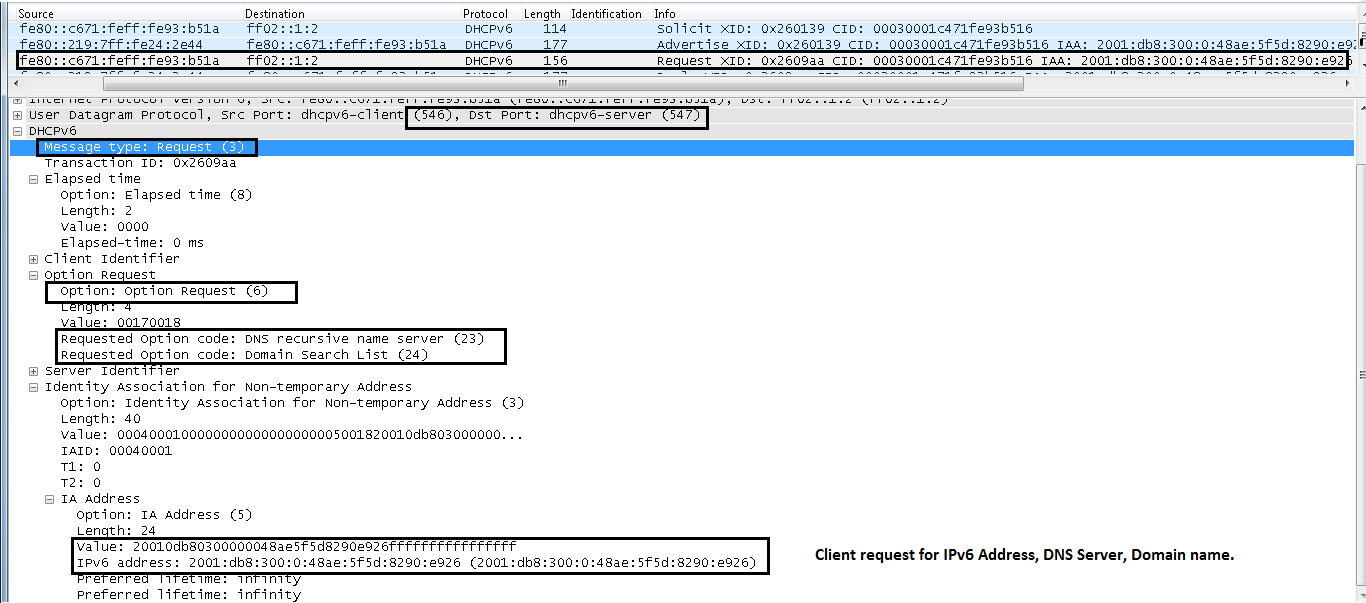
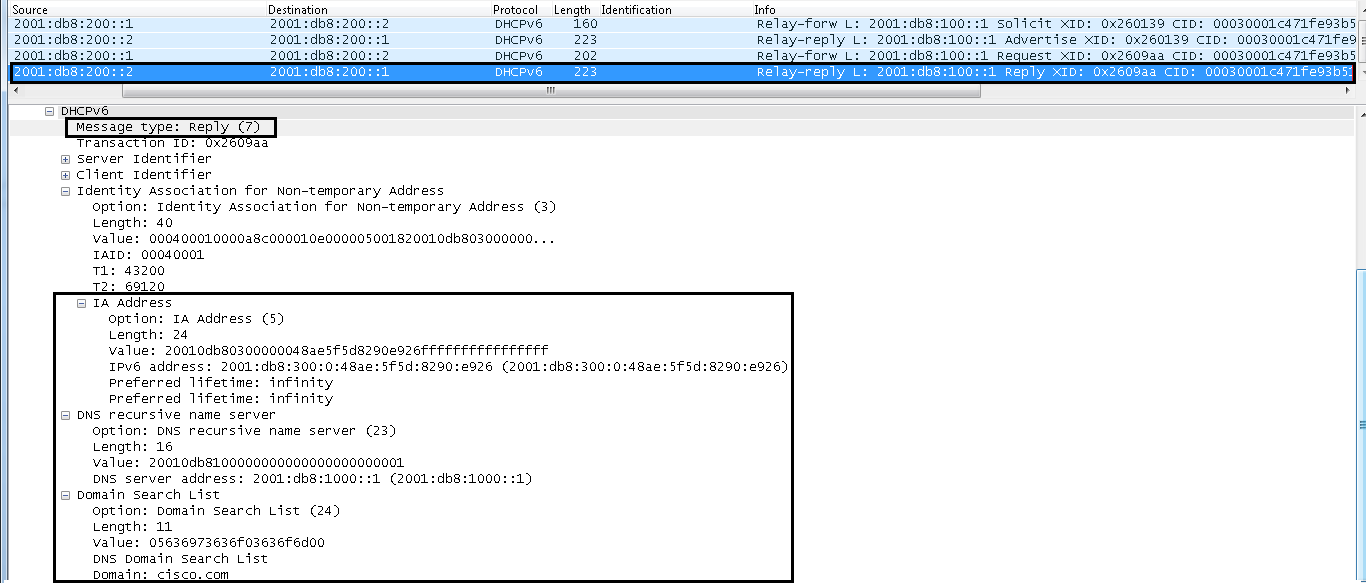
Wireshark Snapshots
DHCP Client Request
DHCP Request Relayed by ASA
DHCP Reply From Server
Reply Forwarded to Client
Stateful DHCPv6
Configuration
Here is the basic configuration for Stateful DHCPv6 relay configuration on the ASA:
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
nameif CLIENT
security-level 100
ipv6 address 2001:db8:100::1/64
ipv6 enable
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
nameif SERVER
security-level 0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:200:1/64
ipv6 enable
!
ipv6 dhcprelay server 2001:db8:200:2 inside
ipv6 dhcprelay enable outside
Packet Flow
With stateful DHCPv6, here is the packet flow from the client:
The ASA intercepts these packets and wraps them into the DHCP relay format:
Verify
Debugs
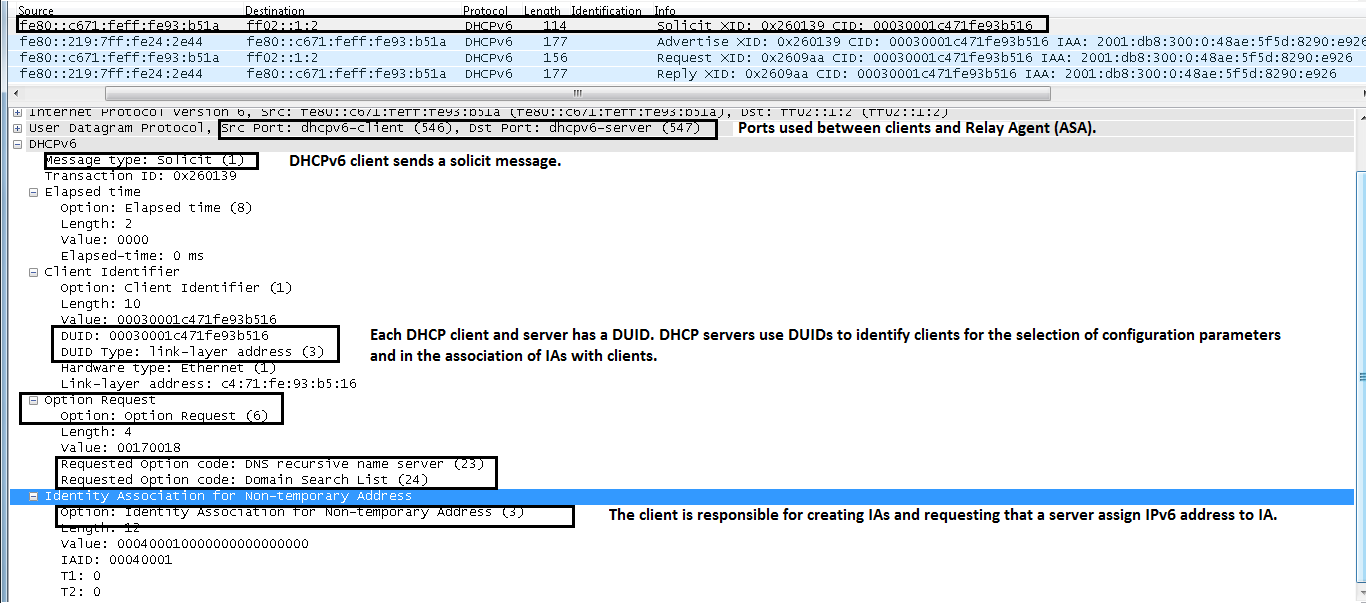
IPv6 DHCP: Received SOLICIT from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
dst ff02::1:2
type SOLICIT(1), xid 2490681
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 4
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST
option IA-NA(3), len 12
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying SOLICIT from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Creating relay binding for fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a at interface CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to 2001:db8:200::2 via 2001:db8:200::2 using SERVER
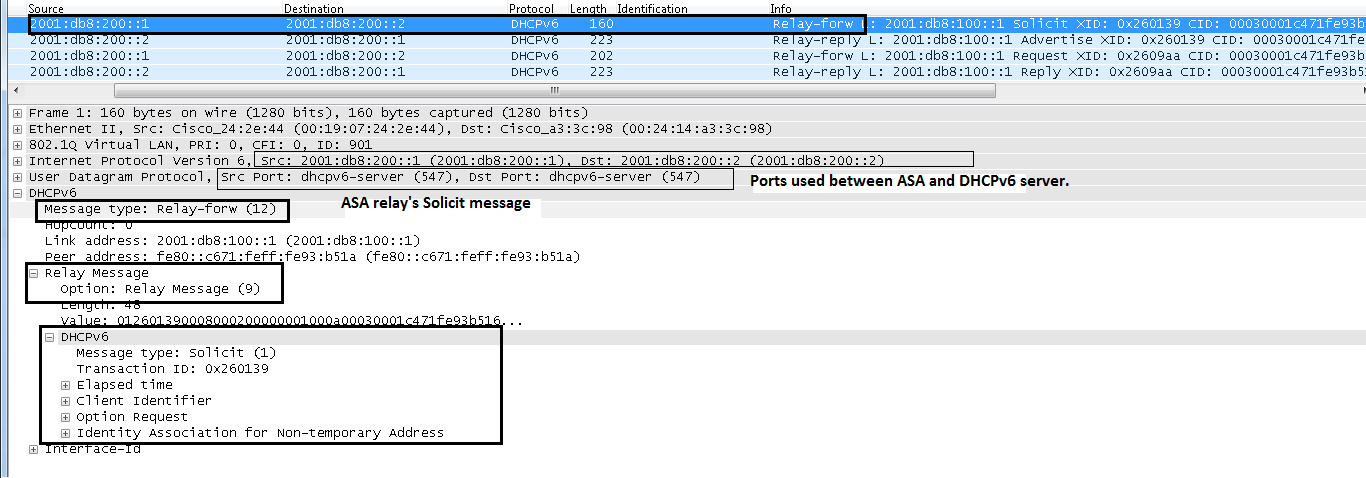
IPv6 DHCP: Sending RELAY-FORWARD to 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::1
dst 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
type RELAY-FORWARD(12), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 48
type SOLICIT(1), xid 2490681
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 4
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST
option IA-NA(3), len 12
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
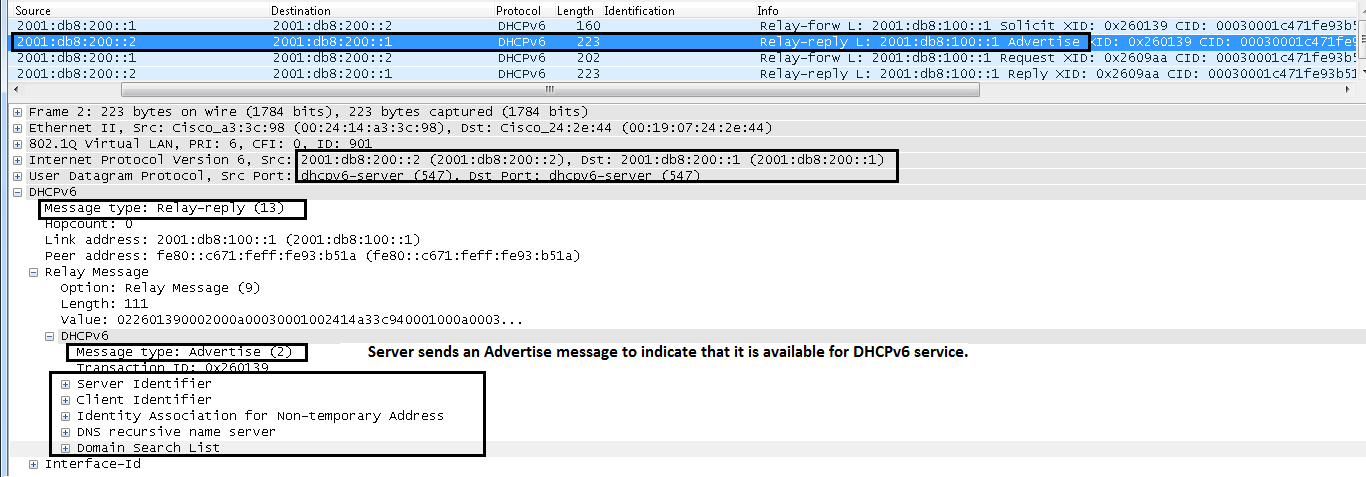
IPv6 DHCP: Received RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
dst 2001:db8:200::1
type RELAY-REPLY(13), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 111
type ADVERTISE(2), xid 2490681
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 43200, T2 69120
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVER
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: relayed msg: ADVERTISE
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
IPv6 DHCP: Sending ADVERTISE to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::219:7ff:fe24:2e44
dst fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
type ADVERTISE(2), xid 2490681
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 43200, T2 69120
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
IPv6 DHCP: Received REQUEST from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
dst ff02::1:2
type REQUEST(3), xid 2492842
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 4
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying REQUEST from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to 2001:db8:200::2 via 2001:db8:200::2 using SERVER
IPv6 DHCP: Sending RELAY-FORWARD to 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::1
dst 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
type RELAY-FORWARD(12), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 90
type REQUEST(3), xid 2492842
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option ORO(6), len 4
DNS-SERVERS,DOMAIN-LIST
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP: Received RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
dst 2001:db8:200::1
type RELAY-REPLY(13), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 111
type REPLY(7), xid 2492842
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 43200, T2 69120
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVER
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: relayed msg: REPLY
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
IPv6 DHCP: Sending REPLY to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::219:7ff:fe24:2e44
dst fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
type REPLY(7), xid 2492842
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 43200, T2 69120
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option DNS-SERVERS(23), len 16
2001:db8:1000::1
option DOMAIN-LIST(24), len 11
cisco.com
Wireshark Snapshots
SOLICIT (1)
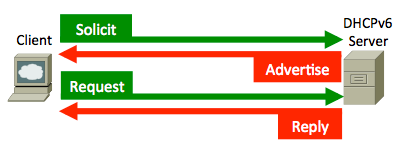
A DHCPv6 client sends a Solicit message in order to locate DHCPv6 servers.
The ASA relays the Solicit message.
ADVERTISE (2)
A server sends an Advertise message in order to indicate that it is available for DHCP service, in response to a Solicit message received from a client.
REQUEST (3)
A client sends a Request message in order to request configuration parameters, which include IP addresses or delegated prefixes, from a specific server.
REPLY (7)
A server sends a Reply message that contains assigned addresses and configuration parameters in response to a Solicit, Request, Renew, or Rebind message received from a client. A server sends a Reply message that contains configuration parameters in response to an Information-request message. A server sends a Reply message in response to a Confirm message that confirms or denies that the addresses assigned to the client are appropriate to the link to which the client is connected. A server sends a Reply message in order to acknowledge receipt of a Release or Decline message.
Troubleshoot
Confirm connectivity with DHCPv6 Server.
ciscoasa# show ipv6 neighbor
IPv6 Address Age Link-layer Addr State Interface2001:db8:200::2 0 0024.14a3.3c98 REACH SERVER
Confirm that you receive packets from the client when it requests an IPv6 address. The packet sent by the client will depend on the address assignment settings (that is, stateful vs stateless).
When the client begins the DHCPv6 process, it sends a Router Solicit message in order to discover the presence of IPv6 routers on the link. It sends a multicast Router Solicitation message in order to prompt the IPv6 routers to respond. In the Ethernet header of the Router Solicitation message, these fields display:
- The Source Address field is the MAC address of the host that requests the IPv6 address.
- The Destination Address field is set to 33-33-00-00-00-02.
In the IPv6 header of the Router Solicitation message, these fields display.
- The Source Address field is set to either a link-local IPv6 address assigned to the sending interface or the IPv6 unspecified address (::).
- The Destination Address field is set to the link-local scope all-routers multicast address (FF02::2).
- The Hop Limit field is set to 255.
In Response, the IPv6 routers send unsolicited Router Advertisement messages The Router Advertisement message contains the information required by hosts in order to determine the link prefixes, the link Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU), and specific routes.
ciscoasa(config)# show capture capin detailfe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a.546 > ff02::1:2.547: [udp sum ok] udp 42
[hlim 255] (len 100)---->Request from clientfe80::219:7ff:fe24:2e44.547 > fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a.546: [udp sum ok]
udp 75 [class 0xe0] (len 133, hlim 255)ciscoasa(config)# show capture capout detail
2 packets captured1: 12:06:52.700799 2001:db8:200:1.547 > 2001:db8:200:2.547: udp 88
[class 0xe0]---->ASA forwards request to DHCPv6 router2: 12:06:53.289047 2001:db8:200:2.547 > 2001:db8:200:1.547: udp 121
[class 0xe0]----> Reply from DHCPV6 server.
DHCP Relay Outputs
ciscoasa# show ipv6 dhcprelay binding
1 in use, 1 most usedClient: fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
DUID: 00030001c471fe93b516, Timeout in 56 seconds
Note: The binding is deleted by the ASA after a short period. This is seen in debug ipv6 dhcprelay.
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Deleting binding for fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a at interface CLIENT
ciscoasa# show ipv6 dhcprelay statisticsRelay Messages:
SOLICIT 2
ADVERTISE 2
REQUEST 2
CONFIRM 0
RENEW 0
REBIND 0
REPLY 9
RELEASE 1
DECLINE 0
RECONFIGURE 0
INFORMATION-REQUEST 6
RELAY-FORWARD 11
RELAY-REPLY 11Relay Errors:
Malformed message: 0
Block allocation/duplication failure: 0
Hop count limit exceeded: 0
Forward binding creation failure: 0
Reply binding lookup failure: 0
No output route: 0
Conflict relay server route: 0
Failed to add server input rule: 0
Unit or context is not active: 0Total Relay Bindings Created: 8
Release Addresses
Clients can release their DHCPv6 assigned address after they are done using it for the network. The next section shows the debug output associated with address release in Stateful DHCPv6.
Debugs
IPv6 DHCP: Received RELEASE from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
dst ff02::1:2
type RELEASE(8), xid 3180815
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying RELEASE from fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Creating relay binding for fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a at interface CLIENT
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to 2001:db8:200::2 via 2001:db8:200::2 using SERVER
IPv6 DHCP: Sending RELAY-FORWARD to 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::1
dst 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
type RELAY-FORWARD(12), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 82
type RELEASE(8), xid 3180815
option ELAPSED-TIME(8), len 2
elapsed-time 0
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option IA-NA(3), len 40
IAID 0x00040001, T1 0, T2 0
option IAADDR(5), len 24
IPv6 address 2001:db8:300:0:48ae:5f5d:8290:e926
preferred INFINITY, valid INFINITY
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP: Received RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVERIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src 2001:db8:200::2 (SERVER)
dst 2001:db8:200::1
type RELAY-REPLY(13), hop 0
link 2001:db8:100::1
peer fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
option RELAY-MSG(9), len 45
type REPLY(7), xid 3180815
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option STATUS-CODE(13), len 9
status code SUCCESS(0)
status message: SUCCESS
option INTERFACE-ID(18), len 4
0x00000015
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: Relaying RELAY-REPLY from 2001:db8:200::2 on SERVER
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: relayed msg: REPLY
IPv6 DHCP_RELAY: to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a
IPv6 DHCP: Sending REPLY to fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a on CLIENTIPv6 DHCP: detailed packet contents
src fe80::219:7ff:fe24:2e44
dst fe80::c671:feff:fe93:b51a (CLIENT)
type REPLY(7), xid 3180815
option SERVERID(2), len 10
00030001002414a33c94
option CLIENTID(1), len 10
00030001c471fe93b516
option STATUS-CODE(13), len 9
status code SUCCESS(0)
status message: SUCCESS
Related Information
Understanding Various DHCP Options
ASA DHCP Relay Configuration Example
Configure the ASA to Pass IPv6 Traffic
ASA Packet Captures with CLI and ASDM Configuration Example
The IP helper-address is set to the DHCP server’s IP address. It is assumed that the reader has some basic knowledge of IP configuration. If you want to configure a DHCPv6 server with multiple routers using Packet Tracer, you cannot use IP helper as there is no IP helper for IPv6. Instead, you can create a local pool, but this may not work. For instance, if the IP address of the interface where you configure the ip-helper address is 10.1.0.254/24, then the DHCP server must have a scope to release IP for 10.1.0.x/24. Note that the ip helper-address tells the router to pass broadcast packets. There are two solutions given. Solution 3 is a blank comment. Solution 4 involves configuring the router and switch. Firstly, configure the router with the following commands: ‘ip dhcp pool POOL_VLAN2X’, ‘relay source’, ‘dhcp-pool-range’, ‘*subnetmask*’, and ‘relay destination *dhcp_server_ip*’. Secondly, configure the switch by typing ‘interface VlanX’ followed by ‘ip address’.
Table of contents
- Will DHCP Relay work across different subnets?
- Why command «ipv6 dhcp relay» doesn’t work at packet tracer?
- DHCP relay Configure in Cisco Router
- How Can I configure DHCPv6
- How do I configure a DHCP relay on a Cisco router?
- What is the IP address of the DHCP relay agent?
- How does a DHCP relay switch work?
- How many DHCP relay agents do I need for DHCP failover?
Will DHCP Relay work across different subnets?
Question:
Network:
- The LAN subnet of Actiontec router provided by ISPs is divided into /25.
- The Cisco RV130 has been subdivided into a /25 subnet. Here are some additional details:
- WAN port to Actiontec LAN port
- set as Gateway, Router mode would not allow internet response.
- ping OK out
,
, and
.
My expectation was to achieve connectivity between the first and second subnets while preserving internet access through enabling Dynamic Routing (RIP) and configuring
DHCP Relay
in Router mode.
Although my eventual plan is to bridge this modem, I am currently using it to test its capabilities for future reference. None of the suggested Similar Questions are relevant to my situation, and I have not yet considered VLANs. This is why I initially set up the router to work with a managed switch on my LAN.
The provided link is for the emulator of the interface that I am currently working with. However, it should be noted that my interface is not wireless in nature. The emulator can be accessed at http://www.cisco.com/assets/sol/sb/RV130W_Emulators/RV130W_Emulator_v1-0-1-3_20140807/default-asp.htm.
I trust that this is straightforward enough for us to talk about in this setting.
Solution 1:
Is it possible for
DHCP relay
to function on various subnets?
The purpose of
dhcp relay
is to utilize DHCP relay, which transforms the broadcasted DHCP discovery message into a unicast packet that is directed towards the
dhcp server
.
Enabling Router mode would result in the Gateway being unable to respond to internet requests.
and
My expectation was that by utilizing DHCP Relay, Router mode, and enabling Dynamic Routing (RIP), I could establish communication from the first subnet to the second while still maintaining internet connectivity within the second subnet.
It appears that your query is not related to DHCP relay. Instead, you seem to be inquiring about the reason behind the unavailability of internet access from the second subnet when your Cisco device is configured as a router.
I’m curious about how the Actiontec router recognizes the subnet beyond the Cisco device. Is there a possibility that it employs a
dynamic routing protocol
and if so, have you configured it accurately on both devices? Also, have you set up a
static route
?
cannot ping into Cisco subnet
Based on the given statement and the fact that it only works when Cisco is acting as a gateway, it appears that the Actiontec device is unsure where to direct the traffic intended for your secondary subnet.
If the Cisco device functions as a router, the Actiontec device is only cognizant of the WAN and LAN subnets that are directly connected. Any traffic intended for any other unsanctioned subnets, such as your secondary subnet, is then routed to its default route, which would be upstream.
As a gateway, the Cisco device is performing NAT on the traffic destined for
IP address
located on the initial subnet. As a result, the Actiontec can easily forward the traffic since it is local.
Solution 2:
Is it possible for DHCP Relay to function between subnets that are not the same?
That is the point of DHCP relay.
It appears that either NAT is being used on
Cisco router
or there is no route configured in
ISP router
to acknowledge the network’s presence on the other end of
Cisco Router
. In either case, accessing the network beyond the Cisco router from the ISP router will not be possible.
Solution 3:
Once you have routed your subnets, it is important to test them. To do this, configure your computer with a specific IP address, which we will call
static IP
, and then try pinging the designated address, known as
DHCP server
, from all the VLANs. It is essential to ensure that this ping test is successful before moving forward.
To enable DHCP on a subnet that is not the same as the DHCP server’s subnet, add
ip helper 10.10.10.10
(the DHCP server’s address) to the gateway of the Cisco router on the interface or sub-interface of the VLAN that differs from the DHCP server. This process should be repeated for each gateway that needs to forward DHCP requests across subnets. By doing so, the UDP broadcast can reach the server, despite the layer 3 boundary that typically prevents broadcasts.
Construct a
dhcp scopes
for every subnet on your DHCP server, which will allocate addresses according to the subnet from which the request was made.
Cisco — How are two «ip helper-address» statements, For redundancy, but to not violate the DHCP rule of not having overlapping scopes defined for your IP pools, you need two ip-helpers. Since the DHCP servers are not aware of one another, the IP pools must be unique. A common method for DHCP redundancy is to take your typical /24 subnet and divide it into two /25s for your …
DHCP relay using Cisco packet tracer
We demonstrate
DHCP relay
using
cisco
packet tracer in this video.#DHCPrelay#IPhelperaddress.
DHCP relay not working Cisco
This is a quick video on an issue I ran into recently where
DHCP
clients were not obtaining addresses even though the router had ip-helper statements configu
How to Configure DHCP Relay Agent on Cisco Routers in
How to Configure
DHCP Relay
Agent on
Cisco
RoutersThis tutorial explains the
DHCP relay
agent configuration in detail. Learn how to use the ‘ip helper-addres
Why command «ipv6 dhcp relay» doesn’t work at packet tracer?
Question:
I’m attempting to activate dhcp for ipv6 utilizing the «ipv6 dhcp relay dest» function, however, an error is appearing. Despite trying both commands, none seem to be effective.
Model of the router:
2811
(config)# interface [interface-1]
(config-if)# ipv6 dhcp destination [destination ipv6 address]
[interface-2]
and
interface type number
The interface-number is specified as the destination for the ipv6 dhcp relay, labeled as
address [interface
.
Error:
% invalid input detected at ‘^’ marker
.
Source
Solution 1:
Considering the 2811 router’s age, it has been End-of-Life since 2016 and the last software updates were released in 2014, which is over four years ago. Therefore, it is likely that your IOS version does not support this command. To determine if the command is supported, it is important to check the IOS versions where it was introduced.
The IPv6 Command Reference for Cisco IOS includes information on the configuration of the «ipv6 dhcp relay destination» command.

The subject matter does not appear to be at the CCNA level and Packet Tracer, an emulator with limited capabilities, may not provide support. It is possible that a genuine 2811 router could run the appropriate IOS version, although it may not be available due to the router’s EoS status.
Solution 2:
For those who come across this query, it’s worth noting that Packet Tracer does not support the implementation of IPv6
Relay Agent
for any router.
14 Configure DHCP Relay Agent in Cisco ASA firewall, Lecture 14: Configuring
DHCP
server
Relay
Agent in
Cisco
ASA firewall with IP helper address configuration on
cisco
switch. In this video I shown you that h
DHCP relay Configure in Cisco Router
Question:
I am attempting to set up the relay command on my Cisco device, specifically
Router dhcp
. However, my router seems to be unable to execute this configuration.
Solution 1:
To configure the DHCP scope on the remote
dhcp servers
, make sure that the pool is located on the identical subnet as the configured interface.
Execute the given instructions on the designated interface.
interface vlan 1 ip helper-address ****.**** ip helper-address ****.**** ip directed-broadcast
In step 3, verify whether there is access on the designated interface. If affirmative, permit the passage of UDP traffic through
port 67
and
udp 68
.
Solution 2:
To configure a specific interface on a Cisco Router, use the following command.
The «ip helper-address» command is used to specify an alternate subnet address.
Ensure that your DHCP server is configured with a scope that releases IP addresses in the same subnet as the router interface. For instance, if the IP address of the router interface where
ip-helper address
is configured is 10.1.0.254/24, then the DHCP server must have a scope that releases IP addresses for the subnet 10.1.0.x/24.
The
ip helper-address
note instructs the router to allow the passage of
broadcast packets
, which will then be taken. It’s a straightforward process.
Solution 3:
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#ip dhcp pool IT ["as you like you can change name"]
Router(dhcp-config)#network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 ["as you like you can change network"]
Router(dhcp-config)#default-router 192.168.1.1 ["this router ip"]
Router(dhcp-config)#dns-server 192.168.1.100
Router(dhcp-config)#exit
Router(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0/0
Router(config-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#no shutdown
Router(config-if)#exit
Router(config)#exit
Router#write memory
[«»] This is mean comment
Solution 4:
In the Router’s configuration, set up
ip dhcp
by creating a pool called POOL_VLAN2X and specifying the source for the relay. Then, define the range of IP addresses for the DHCP pool and the subnet mask. Finally, specify the destination for the relay as the IP address of the DHCP server.
In the Switch Configuration, set up the VlanX interface with an IP address of ****.**** ****.****. Then, include the
ip helper
and specify the *dhcp_server_ip* as the address.
Anticipating a fundamental understanding of IP configuration.
DHCP relay not working Cisco, This is a quick video on an issue I ran into recently where
DHCP
clients were not obtaining addresses even though the router had ip-helper statements configu
How Can I configure DHCPv6
Question:
In Packet Tracer, I aim to set up a DHCPv6 server for multiple routers to distribute
IP addresses
to computers. Previously, I achieved this with IPv4 using
IP Helper
, but since there is no IP helper for IPv6, I need to find an alternative approach.

Despite my efforts to create a local pool, it proved to be ineffective.
Would you be able to clarify and assist me in comprehending the subject at hand? Additionally, could you kindly refer to the attached image, labeled as
, to aid in the explanation?
Solution 1:
You have two options
-
As per Ron Maupin’s instructions, establishing a
DHCP relay agent
is required. - To configure an IPv6 pool on your Cisco router.
DHCP relay agent
> Activate
Enter the configuration terminal.
The command prompt appears as «(config)#» and can be used to configure settings for a specific interface, which is identified by the name «[interface-1]».
On the configuration interface, enter the command «ipv6 dhcp destination» followed by the destination IPv6 address and the interface number, which is «interface-2».
The code snippet ends with the command «end» entered in the interface configuration mode.
The interface assigned with the DHCPv6 address is referred to as interface-1, while interface-2 is designated as the relay interface.
Bear in mind that the assigned address for your
relaying interface
must be routable for it to function effectively.
To view the details of the address that has been received:
# show ipv6
dhcp interface
Stateful configuration by Cisco Routers
(config)#
ipv6 unicast-routingAt the configuration prompt, you can create an IPv6 DHCP pool with a specified name by using the command «ipv6 dhcp pool [pool name]».
At (config)#, input «addreess prefix [IPV6 \64] lifetime infinite inifinite» to set the prefix address with an infinite lifetime.
In the configuration, specify the IPv6 address of the DNS server using the command «dns-server».
In the configuration, the domain name is set to [mydomain.org] with the command «domain-name».
To assign an interface to the pool:
On the configuration interface, use the command «ipv6 dhcp server [pool name]» to set up the DHCP server for IPv6.
Within the «conifg-if» mode, execute the command «ipv6 enable [mode]-commit» to activate IPv6.
The mode for commit can be either rapid or normal, and a possible prefix example is 2010:BB:BB:11::/64.
More information at:
-
A guide on IP Addressing for Cisco IOS Release 15M&T is available under the code name
DHCP Configuration
. - The introduction of IPv6 requires the implementation of DHCP specifically designed for this protocol.
Solution 2:
Explore the interface command
ipv6 dhcp relay destination
and investigate various options for Router Advertisements (RAs). Cisco offers extensive documentation on the topic of IPv6 addressing, such as «Implementing DHCP for IPv6». With IPv6, you have a wider range of options available, such as adding
prefix delegation
to your routers.
Configuring the DHCPv6 Relay Agent
The following steps provide a summary.
enable
- Enter the configuration terminal.
- Number type for an interface.
- Specify the destination for ipv6 DHCP relay by providing an ipv6 address along with an optional interface type and number.
end
Configuring DHCP Relay on Cisco ASA, About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features
Press Copyright
Contact us …
- Remove From My Forums
-
Вопрос
-
Hi all,
The situation is the following:
— Dualstack Windows Server 2012 (SRV01) with DHCP role configured in VLAN 10.
— Dualstack Windows 10 (LAP01) configured in VLAN 20
— Camera (CAM01) configured in VLAN 20
— Cisco router (RT01) intervlan routing VLANS IPv4 and IPv6SRV01 (VLAN 10):
10.21.100.97 /27
FC00::2/64
DHCP scope: Range: FC03::
Exclusion: FC03::1CAM01 (VLAN 20):
10.21.100.33 /27
FC02::20/64
conf (GUI):
IPv6 enabled — CHECK
Accept router advertisements — CHECK
DHCPv6 — STATEFUL/STATELESS/AUTO/OFFLAP01 (VLAN 30):
10.21.100.65 /27
FC03::30/64RT01:
DG VLAN 10/20/30 IPv4/IPv6
Relevant IPv6 conf:
— Version 15.5
— ipv6 unicast routing
— interface GigabitEthernet0/0.10
encapsulation dot1Q 10
ipv6 address FC00::1/64
ipv6 enable
— interface GigabitEthernet0/0.20
encapsulation dot1Q 20
ipv6 address FC03::1/64
ipv6 enable ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
ipv6 dhcp relay destination FC00::2
— interface GigabitEthernet0/0.30
encapsulation dot1Q 30
ipv6 address FC03::1/64
ipv6 enable ipv6 nd managed-config-flag
ipv6 dhcp relay destination FC00::2It works perfect when IPv4 and IPv6 are statically configured, just as DHCP IPv4 (ip helper-address).
For DHCPv6, I’ve configured the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag and ipv6 dhcp relay destination commands on the Cisco router. Now, I’d like DHCPv6 to lease an IPv6 address to my Windows 10 cliënt (LAP01). That’s where it goes wrong. The server itself and CAM01
can receive a DHCPv6 address, so the DHCP role is configured properly.
I ran wireshark on a SPAN port and can verify that LAP01 only receives DHCPv6 Solicit and Advertise and router Advertisement and Solicitation.I think it’s a Windows problem, because the CAM01 DOES receive an IPv6 address from the DHCPv6 server…Hopefully someone can help me out! Suggestions are welcome and if more information is requested, feel free to ask!
Kind regards,
TomEDIT: sorry for the lay-out, can’t edit it properly because there are no fonts and fontsizes in the edit-tool
-
Изменено
9 января 2017 г. 13:55
-
Изменено