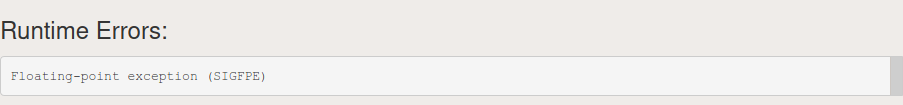
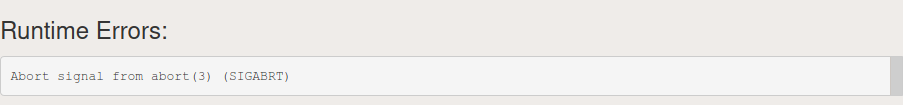
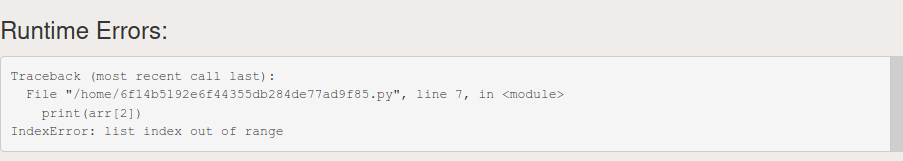
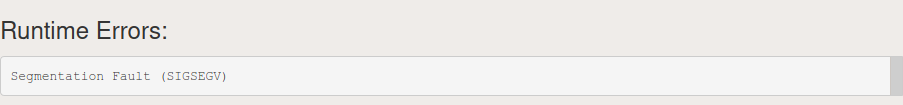
Ну вот в чем может быть причина?
На компьютере программа работает (по крайней мере уж точно выполняется), а здесь выдает вот такую ошибку.
Задачка 551.
Язык: java
Код:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Block {
//Bloc length and module value
static int amountOfBloc, modValue;
//Array input first bloc
static String [] arDataInBloc;
//Array control bloc
static int [] arControlBloc;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String delims = «[ ]+»;
//sum of values input bloc
int sumOfInputBloc = 0;
//input data string
String inputString = Entering();
//input data array
String [] inputArray = inputString.split(delims);
amountOfBloc = Integer.parseInt(inputArray[0]);
if ((amountOfBloc<1)||(amountOfBloc)>1000) {
//System.out.println(«1<=N<=1000»);
System.exit(0);
}
modValue = Integer.parseInt(inputArray[1]);
if ((modValue<2)||(modValue)>1000000000) {
//System.out.println(«2<=M<=10^9»);
System.exit(0);
}
inputString = «»;
inputString = Entering();
arDataInBloc = inputString.split(delims);
if (arDataInBloc.length!=amountOfBloc) {
//System.out.println(«Amount of block is not «+amountOfBloc);
System.exit(0);
}
for (int i=0; i
sumOfInputBloc += Integer.parseInt(arDataInBloc[i]);
if (sumOfInputBloc%modValue!=0) {
System.out.println(«NO»);
System.exit(0);
}
//create control bloc array
arControlBloc = new int [amountOfBloc];
Control ();
}
public static String Entering() throws Exception {
BufferedReader inData = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String dataString = inData.readLine();
return dataString;
}
public static void Control () {
//control variable
int control;
String outString = «»;
//set some value for b1 (look to condition)
arControlBloc[0] = 0;
for (int i=1; i
arControlBloc[i] = (Integer.parseInt(arDataInBloc[i-1])+arControlBloc[i-1])%modValue;
}
control = (arControlBloc[amountOfBloc-1]
+ Integer.parseInt(arDataInBloc[amountOfBloc-1]))
%modValue;
if (control != arControlBloc[0]) {
System.out.println(«NO»);
System.exit(0);
}
else {
for (int i=0; i
outString = outString.concat(arControlBloc[i] + » «);
}
//outString = outString.trim();
System.out.println(«YES»);
System.out.println(outString);
}
}
}

Здравствуйте, помогите, пожалуйста, разобраться. Пытаюсь сдать задачу, из 27 тестов в трех — ошибка во время выполнения программы.
Условие:
Кликните здесь для просмотра всего текста
Как и у каждого мальчика, у Феди есть игрушечные машинки. Однако ему повезло больше, чем обычному мальчику — все n его машинок являются радиоуправляемыми. Целыми днями он может устраивать различные автогонки и играть с друзьями.
Из всех видов гонок Федя предпочитает гонки по прямой. В данном формате соревнования трасса имеет форму прямой и является бесконечной (соревнования идут до тех пор, пока Феде это не надоест). Изначально каждая из n машинок находится на некотором расстоянии от старта — имеет фору xi метров. По команде все машинки начинают свое движение от старта, при этом каждая машинка движется во время гонки с постоянной скоростью vi метров в секунду. Все машинки движутся в одном направлении — удаляются от старта.
Недавно Феде подарили видеокамеру, и он хочет заснять яркие моменты гонки. Прежде всего Федя хочет запечатлеть первый обгон гонки, то есть первый момент времени, в который две машины находятся на одном расстоянии от старта.
Так как этого события можно ждать очень долго, Федя хочет настроить камеру на автоматическое включение во время обгона. Однако, Федя самостоятельно не может найти время, которое пройдет со времени начала гонки до времени первого обгона. Помогите Феде — напишите программу, находящую искомую величину.
Формат входных данных
В первой строке входного файла содержится единственное число n — количество машинок на трассе (2 <= n <= 100). Каждая из следующих n строк содержит по два целых числа xi и vi — расстояние от старта (в метрах) и скорость машинки i (в метрах в секунду) соответственно (1<= xi,vi <= 1000).
Исходно никакие две машинки не находятся в одной точке. Гарантируется, что хотя бы один обгон во время гонки произойдет.
Формат выходных данных
В выходной файл выведите количество секунд, которое пройдет с момента старта до момента первого обгона, с точностью не менее 5 знаков после десятичной точки.
Решение-то простое, перебираем машинки, ищем пары, где у одной скорость больше, а координата меньше, затем выбираем минимум из решений. Сразу оговорюсь, писал без оптимизаций
| C++ | ||
|
Скорости гарантированно разные при делении, значит, на ноль не должно быть деления… В чём может быть проблема?
Решаю задачу по информатике :
Преподаватель по программированию некоего Центра для одаренных детей,
узнав, что его ученики знают математику 3-го класса на 97.001
процентов, решил проверить их знания по курсу математики 1-го класса.
Для этого он взял за основу популярнейшую у математиков 1-го класса
задачу.
Первоклассник должен был продолжить следующую последовательность рядов:
1
11
21
1211
111221
312211
13112221
Входные данные
В единственной строке входного файла записаны два целых числа через пробел: x(0<=x<=100) — первый член последовательности и n(1<=n<=25).
Выходные данные
Выведите n-ый ряд x-ой последовательности
Примеры
входные данные
1 4
выходные данные
1211
Либо по этой ссылке : https://informatics.msk.ru/mod/statements/view3.php?id=248&chapterid=2796#1
Идея какова: В первой строке число 1 встречается 1 раз. Сначала выводим во вторую строку счетчик, потом число. Во второй получившийся строке число 1 всетрчается 2 раза, поэтому 21. В этой строке число 2 встречается 1 раз и число 1 встречается 1 раз, поэтому 1211. И так далее
Важно, что счетчик считает количество цифр подряд. То есть после 1211 будет
111221 (один раз 1, один раз 2, два раза 2), но не 3112(три раза 1, один раз 2)
Собственно, говоря, мой код:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
stringstream container;
string s[25], c;
int n, counter = 1, i, a;
string counter_s;
string return_next_string()
{ //ФУНКЦИЯ ВЫВОДИТ
container.clear(); //СНАЧАЛА СЧЕТЧИК
container << counter; //А ПОТОМ ЧИСЛО
container >> counter_s; //СЧЕТЧИК УКАЗЫВАЕТ СКОЛЬКО РАЗ ПОДРЯД ВСТРЕТИЛОСЬ ЧИСЛО
s[a+1] = s[a+1] + counter_s + c[i]; //И ТАКИМ ОБРАЗОМ ВВОДИТСЯ СЛЕДУЮЩАЯ СТРОКА
counter = 1;
return s[a+1];
}
int main()
{
cin >> s[0] >> n; //ВВОД САМОЙ ПЕРВОЙ СТРОКИ И ЧИСЛА НУЖНОЙ НАМ СТРОКИ
for ( a = 0; a < n; a++) //ПЕРЕБОР СТРОК С 1 ДО НУЖНОЙ
{
c = s[a];
i = 0;
while (i < s[a].size()) //ПЕРЕБОР КАЖДОЙ ЦИФРЫ В СТРОКЕ
{
if (i == s[a].size() - 1) //ЕСЛИ ЦИФРА ПОСЛЕДНЯЯ
return_next_string();
else if (c[i] == c[i + 1] ) //ЕСЛИ ЦИФРА РАВНА СЛЕДУЮЩЕЙ
counter++; //УВЕЛИЧИВАЕМ СЧЕТЧИК
else //ЕСЛИ ЦИФРА НЕ РАВНА СЛЕДУЮЩЕЙ, ТО ВХОДИМ В return_next
return_next_string(); //и узнаем, сколько раз она была равна
i++;
}
}
cout << s[n-1] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
В чем проблема: Из всех 20 тестов не проходят 2. Причина : ошибка выполнения программы. Какое исключение не обработано, что вызывает ошибку — не могу понять с начала недели. Сдался)
Runtime Errors:
- A runtime error in a program is an error that occurs while the program is running after being successfully compiled.
- Runtime errors are commonly called referred to as “bugs” and are often found during the debugging process before the software is released.
- When runtime errors occur after a program has been distributed to the public, developers often release patches, or small updates designed to fix the errors.
- Anyone can find the list of issues that they might face if they are a beginner in this article.
- While solving problems on online platforms, many run time errors can be faced, which are not clearly specified in the message that comes with them. There are a variety of runtime errors that occur such as logical errors, Input/Output errors, undefined object errors, division by zero errors, and many more.
Types of Runtime Errors:
- SIGFPE: SIGFPE is a floating-point error. It is virtually always caused by a division by 0. There can be mainly three main causes of SIGFPE error described as follows:
- Division by Zero.
- Modulo Operation by Zero.
- Integer Overflow.
Below is the program to illustrate the SIGFPE error:
C++
#include <iostream>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){inta = 5;cout << a / 0;return0;}Output:
- SIGABRT: It is an error itself is detected by the program then this signal is generated using call to abort() function. This signal is also used by standard library to report an internal error. assert() function in C++ also uses abort() to generate this signal.
Below is the program to illustrate the SIGBRT error:
C++
#include <iostream>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){inta = 100000000000;int* arr =newint[a];return0;}Output:
- NZEC: This error denotes “Non-Zero Exit Code”. For C users, this error will be generated if the main() method does not have a return 0 statement. Java/C++ users could generate this error if they throw an exception. Below are the possible reasons of getting NZEC error:
- Infinite Recursion or if you run out of stack memory.
- Negative array index is accessed.
- ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception.
- StringIndexOutOfBounds Exception.
Below is the program to illustrate the NZEC error:
Python
if__name__=="__main__":arr=[1,2]print(arr[2])Output:
- SIGSEGV: This error is the most common error and is known as “Segmentation Fault“. It is generated when the program tries to access a memory that is not allowed to access or attempts to access a memory location in a way that is not allowed. List of some of the common reasons for segmentation faults are:
- Accessing an array out of bounds.
- Dereferencing NULL pointers.
- Dereferencing freed memory.
- Dereferencing uninitialized pointers.
- Incorrect use of the “&” (address of) and “*”(dereferencing) operators.
- Improper formatting specifiers in printf and scanf statements.
- Stack overflow.
- Writing to read-only memory.
Below is the program to illustrate the SIGSEGV error:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>usingnamespacestd;voidinfiniteRecur(inta){returninfiniteRecur(a);}intmain(){infiniteRecur(5);}Output:
Ways to avoid Runtime Errors:
- Avoid using variables that have not been initialized. These may be set to 0 on your system but not on the coding platform.
- Check every single occurrence of an array element and ensure that it is not out of bounds.
- Avoid declaring too much memory. Check for the memory limit specified in the question.
- Avoid declaring too much Stack Memory. Large arrays should be declared globally outside the function.
- Use return as the end statement.
- Avoid referencing free memory or null pointers.
Last Updated :
30 Sep, 2020
Like Article
Save Article
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
#define fip(a) for(int i=0;i<(a);i++)
#define fjp(b) for(int j=0;j<(b);j++)
using namespace std;
class task{
private:
struct vertex{
int v;
int l;
int c;
vertex(const int &v,const int &l,const int &c){
this->v=v;
this->l=l;
this->c=c;
}
vertex(){
}
};
struct final{
int l;
int c;
};
typedef vector<vertex> vv;
typedef vector<final> vf;
vv *g;
vf results;
int N,M;
bool stop;
void read_data_from_file(){
const int TRUCT_WEIGHT=3000000;
int a,b,c,d;
FILE *file=fopen("input.txt","r");
fscanf(file,"%d %d",&N,&M);
g=new vv[N];
fip(M){
fscanf(file,"%d %d %d %d",&a,&b,&c,&d);
d-=TRUCT_WEIGHT; d/=100;
if((d>0)&&(c<=1440)) {
a--;b--;
g[a].push_back(vertex(b,c,d));
g[b].push_back(vertex(a,c,d));
}
}
fclose(file);
stop=false;
}
void deikstra(){
const int INF =10000000;
final *d=new final[N];
fip(N){
d[i].l=INF;
d[i].c=INF;
}
vector<int> p(N);
d[0].l=0;
vector<bool> u(N,false);
fip(N){
int v=-1;
fjp(N) {
if(!u[j]&&(v==-1||d[j].l<d[v].l))
{
v=j;
}
}
if(d[v].l==INF) break;
u[v]=true;
fjp(g[v].size()){
int to=g[v][j].v,
len=g[v][j].l,
cap=g[v][j].c;
if(len>-1)
if(d[v].l+len<d[to].l){
d[to].l=d[v].l+len;
p[to]=v;
if(cap<d[to].c) d[to].c=cap;
//printf("%d or %d real %d\n",d[v].c,d[to].c,cap);
}
}
}
// printf("well done %d from F\n",d[N-1]);
if(d[N-1].l!=INF){
results.push_back(d[N-1]);
vector<int> path;
for(int v=N-1;v!=0;v=p[v])
path.push_back(v);
path.push_back(0);
if(path.size()>0){
int end=path[0];
int last=path[1];
fip(g[last].size()){
if(g[last][i].v==end)
g[last][i].l=-1;
//g[last].erase(g[last].begin()+i);
}
}
else stop=true;
//reverse(path.begin(),path.end());
// fip(path.size()) printf("%d ",path[i]);
} else stop=true;
}
void q_sort(vf &res,const int &low,const int &high){
int i=low;
int j=high;
int x=res[(low+high)/2].c;
do{
while(res[i].c>x) ++i;
while(res[j].c<x) --j;
if(i<=j){
final temp=res[i];
res[i]=res[j];
res[j]=temp;
i++; j--;
}
} while(i<=j);
if(low<j) q_sort(res,low,j);
if(high>i) q_sort(res,i,high);
}
public:
void decide_task(){
read_data_from_file();
bool no_answer=true;
int max=0;
while(!stop)
deikstra();
const int size=results.size();
//if(size>1)
// q_sort(results,0,size-1);
fip(size){
if((results[i].c>max)&&(results[i].l<=1440))
max=results[i].c;
}
/* fip(size){
if(results[i].l<=1400){
printf("%d",results[i].c);
no_answer=false;
break;
}
}
if(no_answer) printf("0");*/
printf("%d",max);
/* fip(results.size())
printf("%d %d\n",results[i].l,results[i].c);
printf("rs %d",results.size());*/
}
};
int main(){
task t;
t.decide_task();
/*vector<int> d;
fip(4) d.push_back(i);
d.erase(d.begin()+1);
fip(d.size()) printf("%d ",d[i]);*/
return 0;
}